What is a Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
A carpal tunnel syndrome is the result of the compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
The median nerve is responsible for sensation of the thumb, index and middle finger. It is also responsible for the motor innervation of thenar muscles, located at the base of the thumb.
The carpal tunnel syndrome is a common pathology which causes pain, a burning sensation, and tingling in the hands.
It is more frequent among women than among men. Most often, it is an idiopathic syndrome, meaning that no specific causes trigger it.
Treatment
The medical treatment of the carpal tunnel syndrome consists mainly in corticoid injections performed in the carpal tunnel. These injections are performed during a consultation, about one centimeter above the carpal tunnel. The goal is to inject the corticoid medication in the carpal tunnel in order to decrease the inflammation around the tendons and to make room around the median nerve. Two to three injections can be performed. But the relief is generally only temporary. A night splint can also be used, in association with analgesic medications.
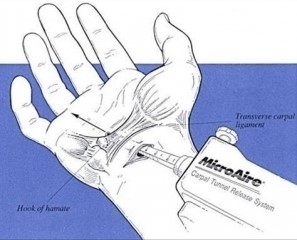
When the medical treatment is not successful, or when the initial extent of the syndrome is too severe, surgical treatment is indicated. The surgical procedure aims at opening the retinacular ligament in order to decompress the median nerve. It can be performed as an open procedure (thus leaving a 2 cm scar in the palm) or as an endoscopic procedure (surgery assisted by a camera, leaving one or two mini-scars).
Most often, the procedure is performed as outpatient surgery under locoregional anesthesia, with no hospitalization.
Once the anterior retinaculum is open, the median nerve can ?regenerate?, The most painful sensations, night pain in particular, usually disappear immediately. However, superficial pain around the area of the scar may subsist longer, and it may take up to three months for all symptoms to disappear. When the procedure is performed through endoscopic surgery, the leave of absence is generally two to three weeks long, whereas it can be longer in the case of open surgery.